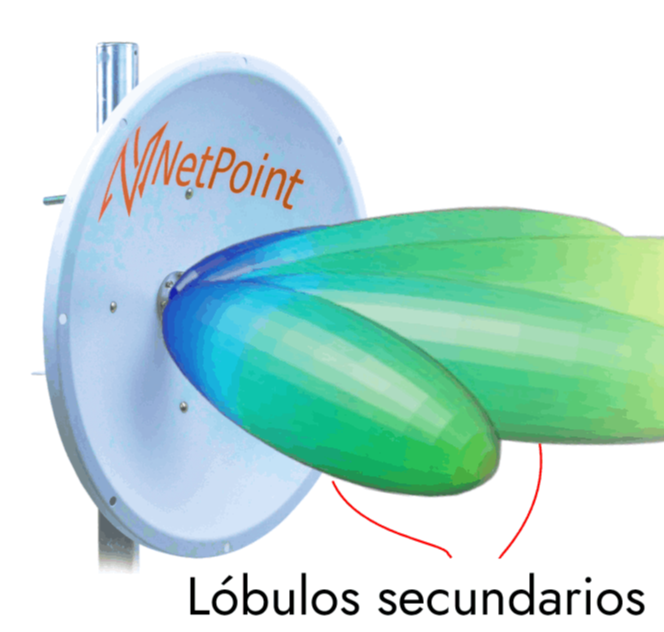
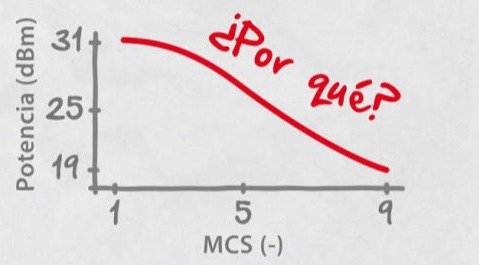
What is the use of the slant in the antennas ?
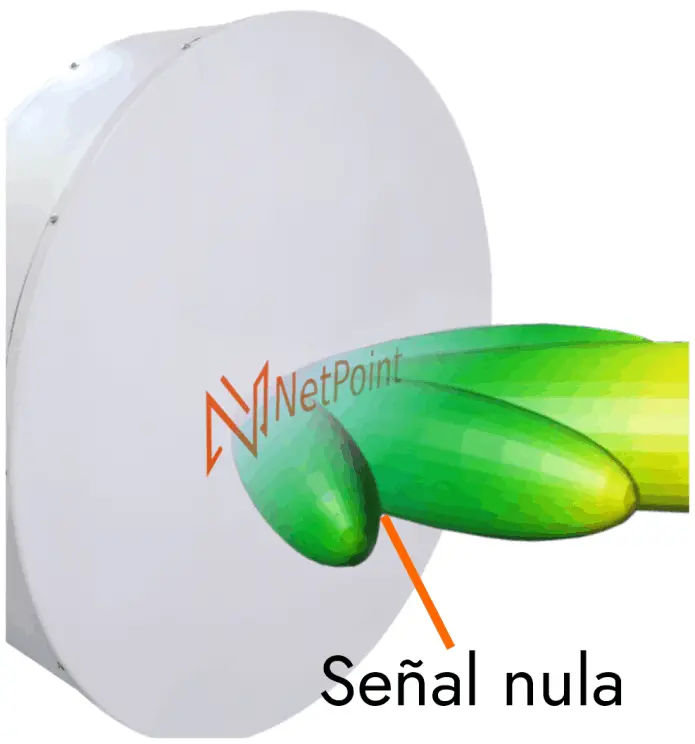
The slant is a term used to describe the tilt or tilt angle of a satellite dish. The slant refers to the vertical distance between the focus of the parabola and its center.
The slant is used to adjust the gain and direction of the satellite dish. A larger slant increases the gain of the antenna and makes it more sensitive to signals arriving from lower angles. On the other hand, a smaller slant decreases the gain of the antenna and makes it less sensitive to signals arriving from lower angles.

Reimagining the works of modernist innovators
The slant is also used to focus the radio frequency signal in a certain direction. Proper slant can help maximize antenna gain and improve RF signal quality.